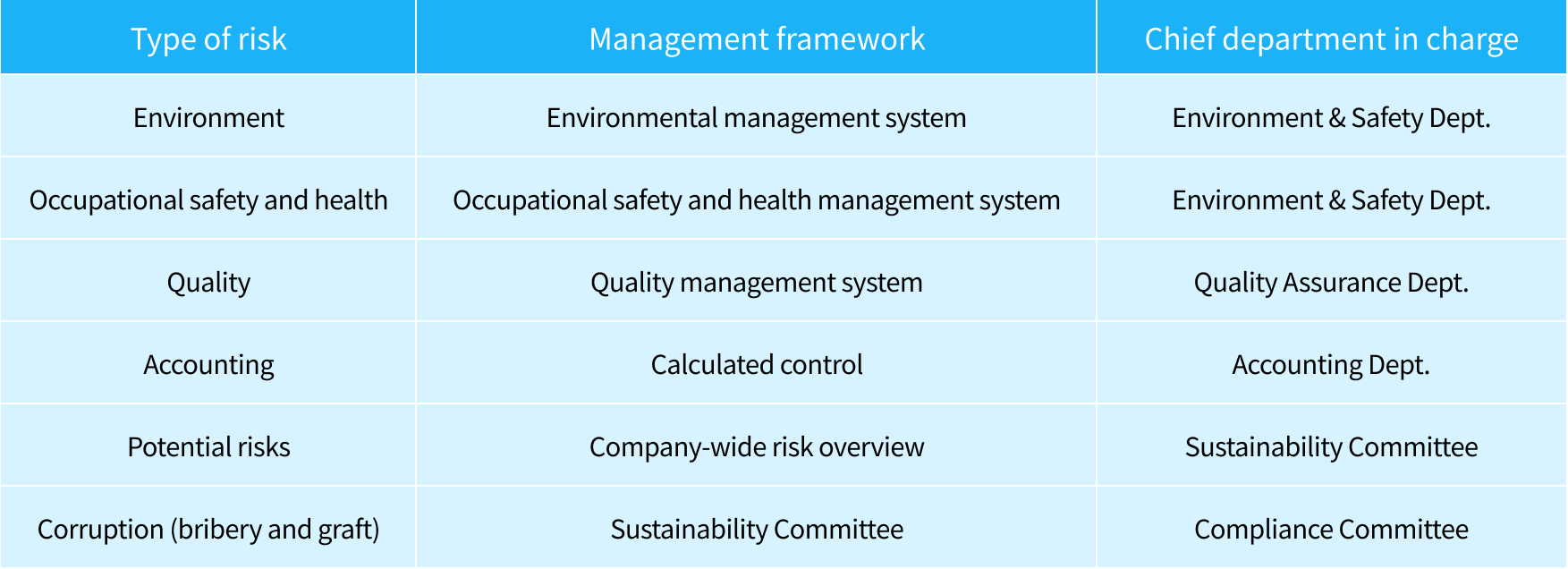
Risk Management
At Fujikura Kasei, we strive to ensure sound and smooth business operations by developing a management framework for preventing risks related to business as a whole and defining methods for responding to risks should they occur.
Our concept of risk management
At Fujikura Kasei, one of our most important management issues is to prevent potential crises by visualizing risks that could hinder our business operations and, in the event a significant risk occurs, to minimize the impact of that risk on our company.
Companies must address both inherent risks and a wide range of risks that vary in scale and frequency. Therefore, we have established a detailed company-wide risk management process. By taking appropriate measures for each risk and mitigating all risks, we aim to achieve sustainable growth and enhance our corporate value.
Risk management framework
We have a long-established risk management framework in place that defines specific measures for each type of risk. As part of our effort to strengthen our sustainability initiatives under the 11th mid-term management plan, the Sustainability Committee discusses and reviews potential company-wide risks as a key management issue.

Identification of company-wide risks and formulation of countermeasures for risk management
As part of our efforts to strengthen our sustainability initiatives under the 11th mid-term management plan, the Sustainability Committee has assumed overall control of potential company-wide risks as a management issue. It has clarified the risks anew from a company-wide perspective and launched initiatives to mitigate those risks.

1. Environmental analysis
Verify the environment surrounding our company from the perspective of achieving sustainable growth and enhancing corporate value.
2. Identify risks (risk identification)
Identify conceivable risks in the operational processes of each department in terms of both external and internal factors (a total of 84 categories of operational risks, financial risks, strategic risks, and hazard risks).
3. Calculate the significance of the risks (risk analysis)
Weigh the identified risks. Create a risk matrix with impact and probability on the two axes. Categorize the risks into share, avoid, accept, and mitigate, with those classified under mitigate as risks that need to be addressed. Risks other than those already covered by existing management systems are considered potential risks.
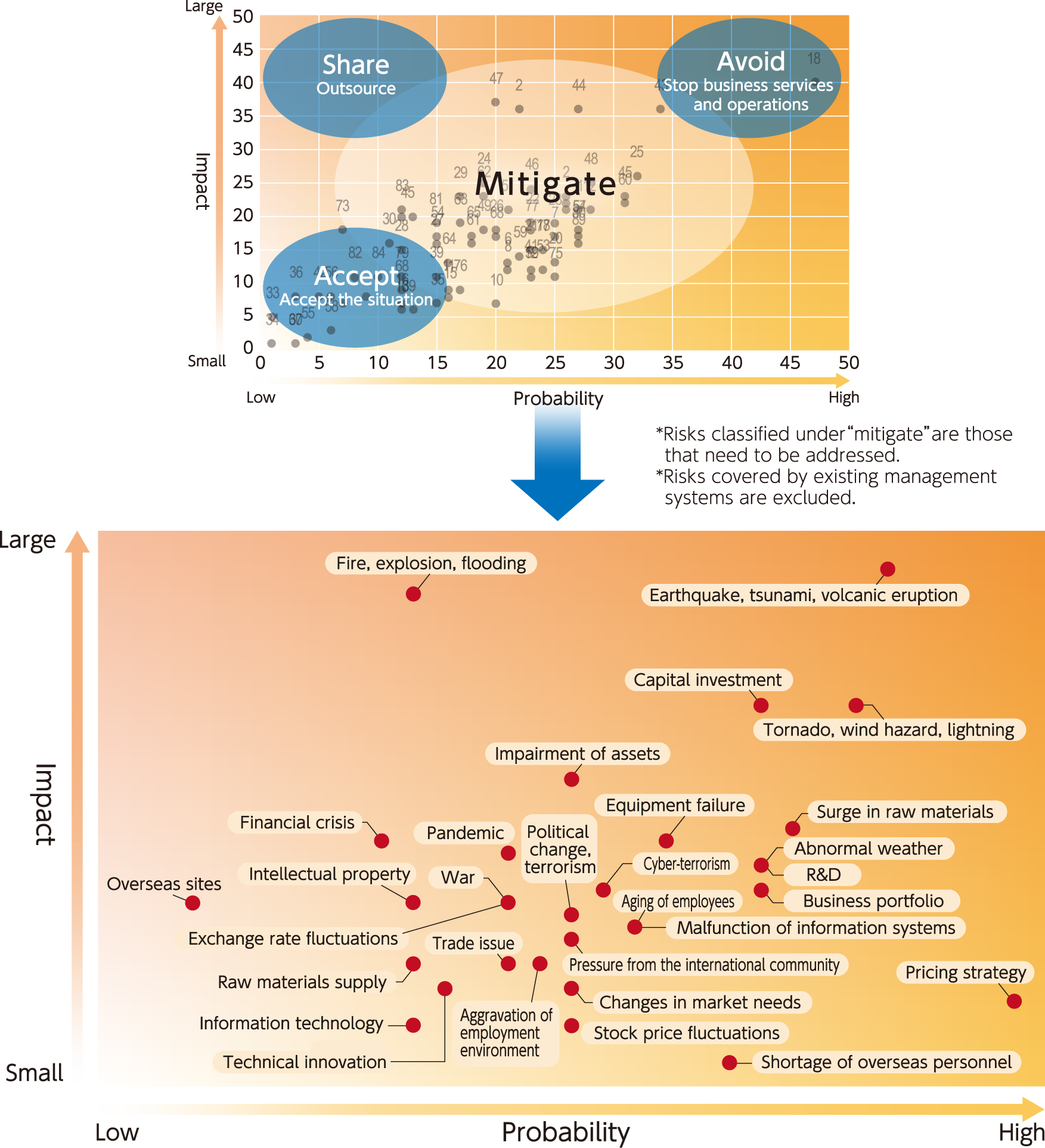
4. Prioritize risk responses (risk evaluation)
Prioritize risks in consideration of various elements.
5. Formulate risk responses
Decide on a risk owner (responsible executive) for each risk item. Make company-wide efforts to mitigate risks.
Under the supervision of the risk owner (the responsible executive), each department explores specific countermeasures for the identified risks that require mitigation and implements these measures by applying the PDCA cycle. The Sustainability Committee regularly discusses and reviews the progress of these efforts to strengthen the company-wide risk management system.
Corporate disaster prevention
We will newly introduce the concept of “corporate disaster prevention” by reconsidering the conventional definition of BCP (business continuity plan), which broadly included “disaster prevention plans” that defined initial responses in the event of a disaster or accident and subsequent“ early recovery plans.” Corporate disaster prevention can be understood as the combination of disaster prevention plans and BCPs, with BCPs placing weight on initiatives for the early recovery of business activities.
Disaster Prevention Plan and Business Continuity Plan (BCP)
Emergency situations—such as natural disasters, man-made disasters, pandemics, and cyberattacks—pose significant risks to business continuity. Corporate disaster prevention refers to the measures a company takes to address these emergencies. Specifically, "disaster prevention" focuses on protecting the physical safety and lives of employees and minimizing damage to company property, while "business continuity" aims to mitigate the impact of emergencies on operations, ensuring the continuation of business activities and facilitating rapid recovery. Corporate disaster prevention involves preparing for both disaster prevention and business continuity. To this end, our company has established a Disaster Prevention Measures Subcommittee to review our disaster prevention plans, as well as a BCP Review Subcommittee to examine our Business Continuity Plan. Each subcommittee is actively working on its respective tasks. Furthermore, to ensure the effective and smooth operation of both our disaster prevention plan and BCP, we have formed the Corporate Disaster Prevention Review Committee. This committee brings together the efforts of both subcommittees to jointly review and adjust our plans as needed.
Information security measures
In recent years, control systems in plants and various other information systems are connected to the Internet, but this connection is increasing the threat of cyberattacks. At Fujikura Kasei, measures against risks identified by the industrial organizations of our business partners have been examined, and information security educational materials (in-house guidelines) have been updated with regard to “production impacts and delivery delays caused by virus infection,”“external leakage of confidential information,”and “springboard attacks by computer viruses via networks.” Measures against information security risks are taken beyond our company to also involve our partner companies. They will be strengthened continuously to reduce information security risks.